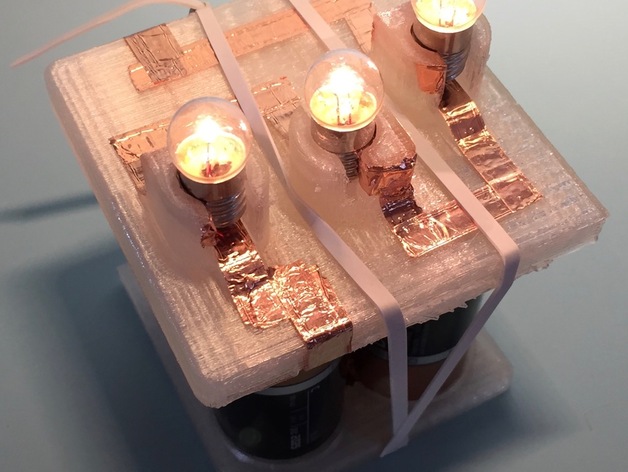
Series and Parallel Circuit Lamp Holders
thingiverse
Here is a revised version of the text with proper formatting and minor edits: **Lesson Plan and Activity** These compact light stations can be used to experiment with, measure, and observe the differences between parallel and series circuits. **Objectives:** * After completing this activity, students will be able to qualitatively and quantitatively explain the difference between series and parallel circuits. * Students will understand the voltage, current, and resistance of their light stations. * Students will learn how various changes to their light stations impact the brightness of the bulbs. **Standards:** * NGSS: + 4-PS3-4. Apply scientific ideas to design, test, and refine a device that converts energy from one form to another. * College Board Standards for AP Physics: + Big Idea 1 - Objects and Systems have properties such as mass and charge. Systems may have internal structure. - Enduring Understanding 1.E: Materials have many macroscopic properties that result from the arrangement and interactions of the atoms and molecules that make up the material. - Essential Knowledge 1.e.2: Matter has a property called resistivity. + Big Idea 3 - The interactions of an object with other objects can be described by forces. - Enduring Understanding 3.C: At the macroscopic level, forces can be categorized as either long-range (action-at-a-distance) forces or contact forces. - Essential Knowledge 3.c.2: Electrical force results from the interaction of one object that has an electric charge with another object that has an electric charge. + Big Idea 5 - Changes that occur as a result of interactions are constrained by conservation laws. - Enduring Understanding 5.B: The energy of a system is conserved. - Essential Knowledge 5.b.9: Kirchhoff’s loop rule describes the conservation of energy in electrical circuits. - Enduring Understanding 5.C: The electric charge of a system is conserved. - Essential Knowledge 5.c.3: Kirchhoff’s junction rule describes the conservation of electric charge in electrical circuits. **Activity:** 1. Introduce the concept of series and parallel circuits to students through lecture or flipping the classroom. 2. Allow students to assemble their lamp holders and "play around" with them. 3. Ask students if they feel the equipment is showing them what they think they should see, based on their prior learning. 4. Encourage a class discussion on what they are seeing, what they'd like to see, and how they could accomplish that. 5. Guide students towards writing the question and hypothesis, then allow them to spend some time developing a procedure and carrying out the remainder of the lab. **References:** * http://www.regentsprep.org/regents/physics/phys-topic.cfm?Course=PHYS&TopicCode=03b * https://www.physics.byu.edu/faculty/rees/220/book/Lesson4.pdf * https://secure-media.collegeboard.org/digitalServices/pdf/ap/ap-physics-inquiry-based-lab-manual.pdf **Rubric and Assessment:** Students will develop a lab report that includes: * Statement of problem * Hypothesis * Background * Procedure * Data table * Graph of data * Data analysis * Error analysis * Conclusion They can communicate this information with a presentation, poster session, or through a written report, depending on your preferences.
With this file you will be able to print Series and Parallel Circuit Lamp Holders with your 3D printer. Click on the button and save the file on your computer to work, edit or customize your design. You can also find more 3D designs for printers on Series and Parallel Circuit Lamp Holders.
