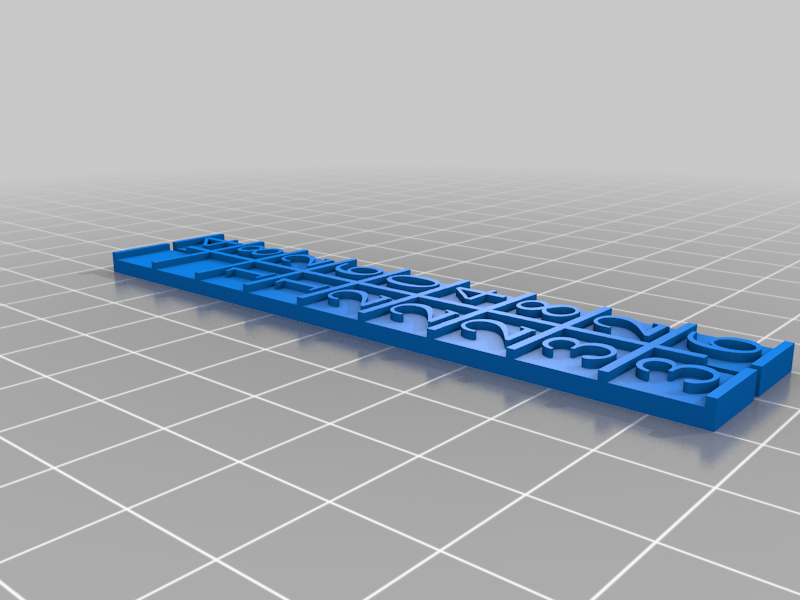
Napier's bones (Bastoncini di Nepero)
thingiverse
John Napier of Merchiston, Scotland created a manually-operated calculating device called Napier's bones. The method was based on lattice multiplication and was also known as Rabdology. In 1617, Napier published his version in Edinburgh, Scotland, dedicating it to his patron Alexander Seton. Using the multiplication tables embedded in the rods, multiplication can be simplified to addition operations and division to subtraction operations. Even more complex use of the rods can extract square roots. Note that Napier's bones are not the same as logarithms, with which Napier is also associated. Here's an example of how to multiply 25 by 4328 using Napier's bones: First, calculate 5 times 4538, then add the result of 20 times 4538. The final step is to add the two results together. First, let's calculate 5 times 4538: This equals 2 times 10000 plus 1 times 1000, plus (5 + 1) times 100, plus 4 times 10, plus 0. That equals 20000 plus 1000 plus 600 plus 50 plus 0. Next, let's calculate 20 times 4538: This equals 8 times 10000, plus 6 times 1000, plus (4 + 1) times 100, plus 6 times 10. That equals 80000, plus 6000, plus 500, plus 60. Finally, let's add the two results together: 20000 plus 1000 plus 600 plus 50 plus 0 equals 21640. And 80000 plus 6000 plus 500 plus 60 equals 86560. Therefore, 25 times 4328 equals 21640 plus 86560. Napier's bones are a unique calculating device that can be used to multiply and divide numbers by adding or subtracting the results of simple multiplication operations.
With this file you will be able to print Napier's bones (Bastoncini di Nepero) with your 3D printer. Click on the button and save the file on your computer to work, edit or customize your design. You can also find more 3D designs for printers on Napier's bones (Bastoncini di Nepero).
