Magnetic Dipole
thingiverse
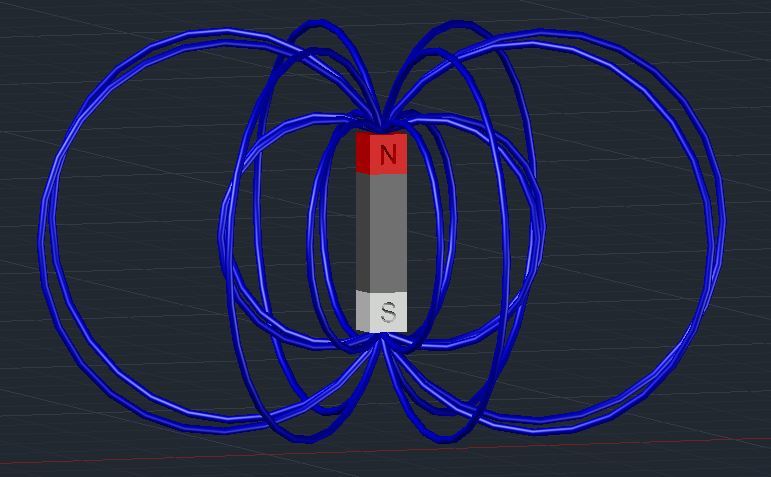
Magnetic forces are generated by magnetic dipoles. A dipole is a pair of magnets, one north and one south pole. The force between two dipoles depends on their distance apart and orientation relative to each other. The magnetic field around a dipole is shaped like a cone with its point at the dipole's location. The magnetic moment of a dipole is defined as the product of the magnetic dipole moment (μ) and the dipole's area (A). It determines how strongly the dipole interacts with an external magnetic field. The magnetic moment can be measured using various methods, including the Hall effect and Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction. The magnetic field around a dipole is strongest at its tip, where it points towards the south pole and away from the north pole. This means that any object placed near a magnetic dipole will experience an attractive force if it's made of a ferromagnetic material like iron or nickel. The strength of this attraction depends on the distance between the object and the dipole. In 3D space, the magnetic field of a dipole can be represented using three components: Bx, By, and Bz. These components are used to calculate the net magnetic force acting on any point in the field. By combining these components, we can visualize the overall shape of the magnetic field around the dipole. Understanding magnetic dipoles is essential for various applications, including navigation systems, medical imaging techniques like MRI, and even some forms of electric power generation.
With this file you will be able to print Magnetic Dipole with your 3D printer. Click on the button and save the file on your computer to work, edit or customize your design. You can also find more 3D designs for printers on Magnetic Dipole.
