
DIP-Clip for In-Circuit Programming/Analyzing ICs
thingiverse
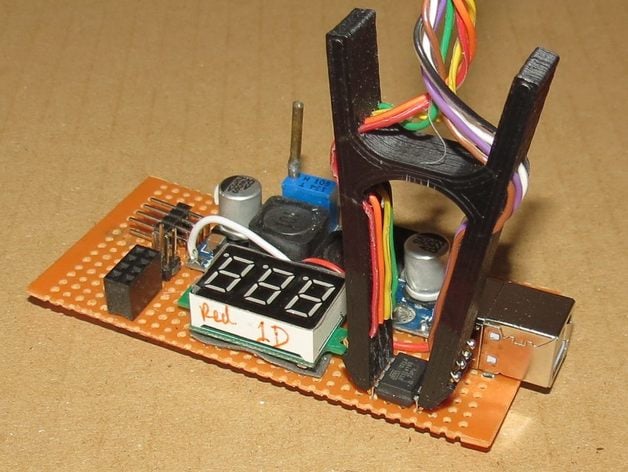
In my projects I often rely on microcontrollers that can be reprogrammed via ISP (in-circuit programming). If there's enough space, I generally incorporate an 8-pin ISP header so I can quickly load new firmware if needed. However, when space is limited, I have to do without an ISP header. So the objective of this project was to design a contact clip for in-circuit analyzing and reprogramming standard DIP ICs with 0.1" pin spacing, which allows me to reprogram microcontrollers and EEPROMs and also debug my developments by analyzing the signals on the pins directly. The contact clips are made from basic pin headers. The bridge in the clip tweezers provides a spring that firmly grips the contacts to the IC. Thin gaps between the pins allow each pin arm to move freely, so the contact force is evenly spread across all pins. The wires leading from the inner rear of the clip through three holes are soldered to the contact headers on the outer front of the clip. For printing, I prefer ABS because it provides the necessary elasticity for movement. To account for the horizontal gaps between the pin arms during printing, explicit supports were generated (shown red in the OpenScad drawing), which need to be carefully cut away with a razor blade or narrow knife after printing. As the pin arms should move smoothly against each other, sometimes I have to use thin sandpaper to "clean" the gaps. The holes for the pin headers and wires are quite precise, so it may be necessary to drill them again for the perfect fit. For the pin header tips, I get my best results with a 0.8mm drill bit. STL files for standard 8-, 14-, 16-, 20- and 28-pin narrow DIP ICs as well as 28- and 40-pin wide DIP ICs are included. Other sizes can be easily generated by modifying the fully parametrized SCAD file. This project wasn't as straightforward as I initially thought, however. The approach presented here is a result of several attempts, from using simple wire loops to pin headers for contacts and ultimately introducing free-swinging pin arms – this was definitely key in making sure good contacts are formed on every single pin consistently... Instructions The Dip-Clips were printed with 3mm ABS filament on my DIY Prusa i3 using a 0.4mm nozzle with an extrusion width of 0.56mm and a layer height of 0.252mm. I print directly onto the clear mirror, thoroughly cleaned it beforehand with acetone and double-concentrated lemon juice but skipped Kapton tape.

With this file you will be able to print DIP-Clip for In-Circuit Programming/Analyzing ICs with your 3D printer. Click on the button and save the file on your computer to work, edit or customize your design. You can also find more 3D designs for printers on DIP-Clip for In-Circuit Programming/Analyzing ICs.
