COAGULATION CASCADE COMMON PATHWAY
sketchfab
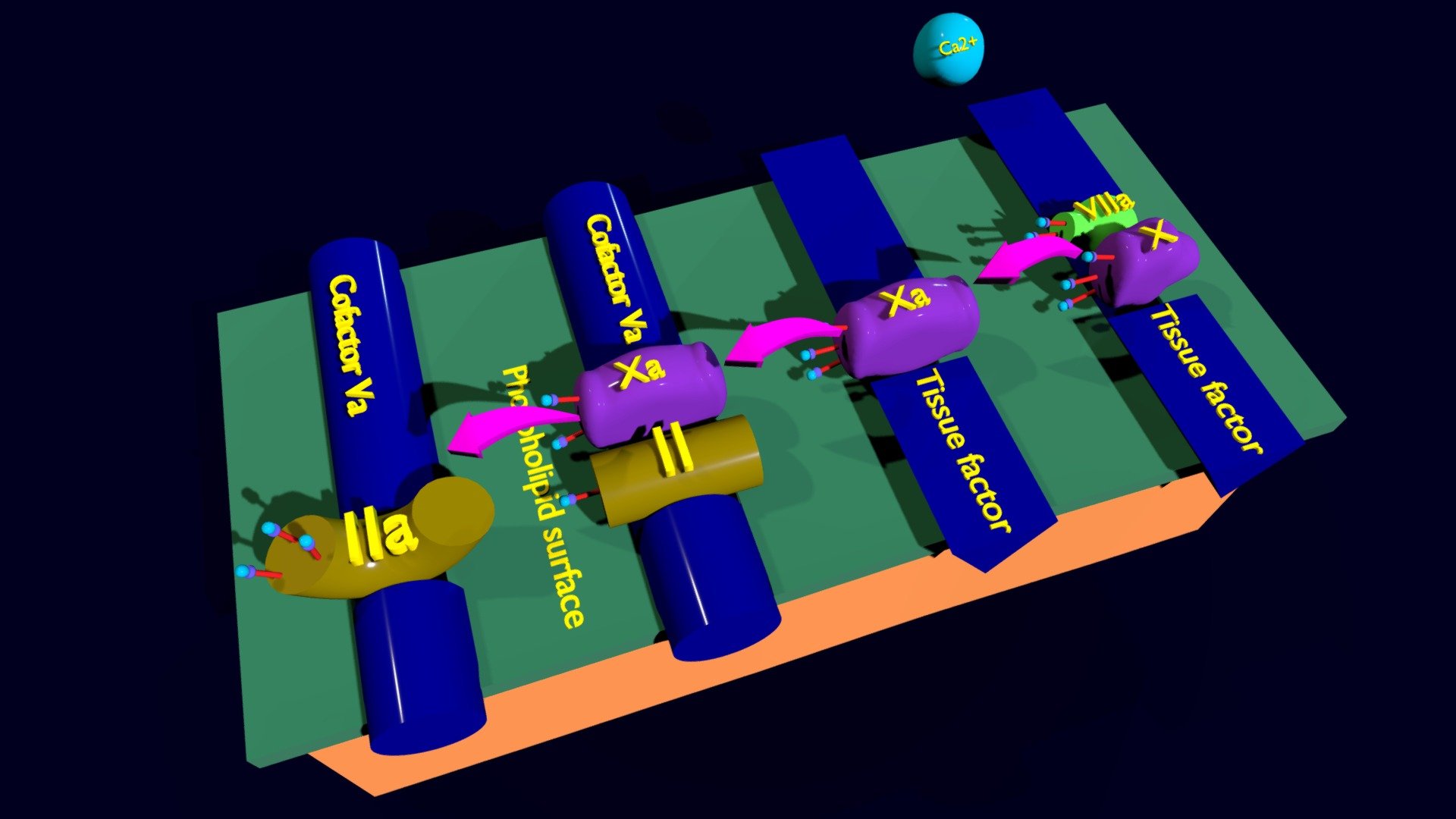
A realistic model portrays a segment of blood clot formation. Made from procedural materials, it doesn't rely on UV maps or image textures. The coagulation cascade is typically divided into intrinsic and extrinsic pathways, both of which merge at the point where factor X is activated, launching the common pathway. A vascular injury exposes tissue factor, which binds with factor VIIa and calcium to prompt the conversion of factor X to Xa. Activated factor X (Xa) combines with its cofactor (factor V), tissue phospholipids, platelet phospholipids, and calcium to form the prothrombinase complex, which converts prothrombin (II) into thrombin (IIa).
With this file you will be able to print COAGULATION CASCADE COMMON PATHWAY with your 3D printer. Click on the button and save the file on your computer to work, edit or customize your design. You can also find more 3D designs for printers on COAGULATION CASCADE COMMON PATHWAY.
