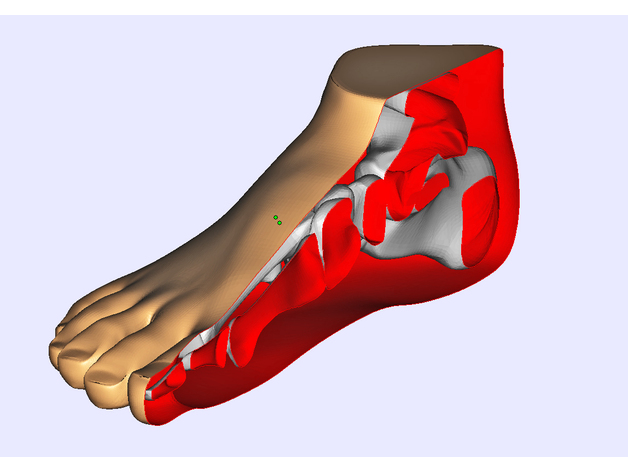
Anatomical Model_Foot
thingiverse
The human foot is an intricate system of bones, muscles, and tendons that work together to support the body's weight and facilitate movement. At its core, the foot consists of 26 bones, which are connected by joints and ligaments. These bones can be divided into three main groups: the tarsal bones, the metatarsal bones, and the phalanges. The tarsal bones form the ankle and provide a base for the foot's weight-bearing structure. The calcaneus is the largest of these bones, serving as a heel bone that connects the lower leg to the rest of the foot. The talus, or ankle bone, sits atop the calcaneus and facilitates movement between the two. The metatarsal bones connect the tarsal bones to the phalanges, forming the arches of the foot. These bones are responsible for distributing weight evenly across the foot and enabling mobility. The first metatarsal bone is longer than the others, allowing it to support the body's weight and facilitate movement. The phalanges, or toe bones, comprise 14 individual bones that make up the toes. These bones work together with the metatarsal bones to form the arches of the foot and provide support for the body's weight. In addition to its skeletal structure, the human foot contains numerous muscles and tendons that facilitate movement and maintain balance. The plantar fascia is a band of tissue that runs along the bottom of the foot, connecting the heel bone to the toes. This fascia helps to support the arches of the foot and facilitates movement. The muscles in the foot are divided into two groups: intrinsic and extrinsic. Intrinsic muscles are located within the foot itself and work together to facilitate movement and maintain balance. The flexor digitorum longus muscle, for example, runs along the bottom of the foot and helps to flex the toes. Extrinsic muscles, on the other hand, are located in the lower leg and work together with the intrinsic muscles to facilitate movement. The tendons that connect the muscles to the bones are also crucial components of the human foot's anatomy. The Achilles tendon connects the calf muscle to the heel bone, facilitating movement between the two. The peroneal tendons run along the outside of the ankle and help to stabilize the joint. In conclusion, the human foot is a complex system that relies on its intricate skeletal structure, muscles, and tendons to facilitate movement and maintain balance. By understanding the various components of this system, we can better appreciate the importance of proper foot care and prevention of injuries such as plantar fasciitis.
With this file you will be able to print Anatomical Model_Foot with your 3D printer. Click on the button and save the file on your computer to work, edit or customize your design. You can also find more 3D designs for printers on Anatomical Model_Foot.
